What is a Binary MLM Plan?
The Binary MLM compensation plan is one of the most recognised models in network marketing. Opinions about it are often divided; some distributors appreciate its unique structure and rules while others prefer plans with more flexibility. Unlike pyramid schemes which depend entirely on recruitment a Binary Plan can offer legitimate products or services making it a valid and sustainable business model.
Along with the Matrix and Unilevel plans, the Binary Plan is one of the three fundamental MLM compensation models and has supported the growth of many businesses. Keep reading to discover how the Binary MLM Plan works and the key benefits and drawbacks of using it in your business.
Streamline Your Binary MLM Plan with Volochain MLM Software
Volochain MLM Software (powered by Maxtra Technologies) is a top MLM software provider in India, offering powerful solutions to manage Binary MLM Plans with ease. As one of the leading Binary MLM software companies, it delivers a robust platform designed to simplify and automate every aspect of the binary compensation structure. With advanced features such as real-time reporting, detailed genealogy tracking, and seamless network management, Volochain’s Binary Plan software is an excellent choice for businesses aiming to scale their network marketing operations efficiently and effectively.
Start your financial success journey with our Binary MLM Plan.
Grab this
opportunity today!
Structure of the Binary MLM Plan
A Binary MLM plan is considered one of the simplest and most user-friendly structures in network marketing. In this model, each member can recruit only two direct downlines on their front line, while the depth of the network can grow infinitely. This means a distributor only needs to enroll two frontline members to begin earning. When someone recruits more than two people, the extra recruits are placed as spillover in the next available positions down the team structure. As the network expands, a two-leg hierarchy grows level by level, creating a continuous two-by-two formation. Since there is no limit to how deep the structure can go, the Binary MLM plan allows unlimited levels of growth.
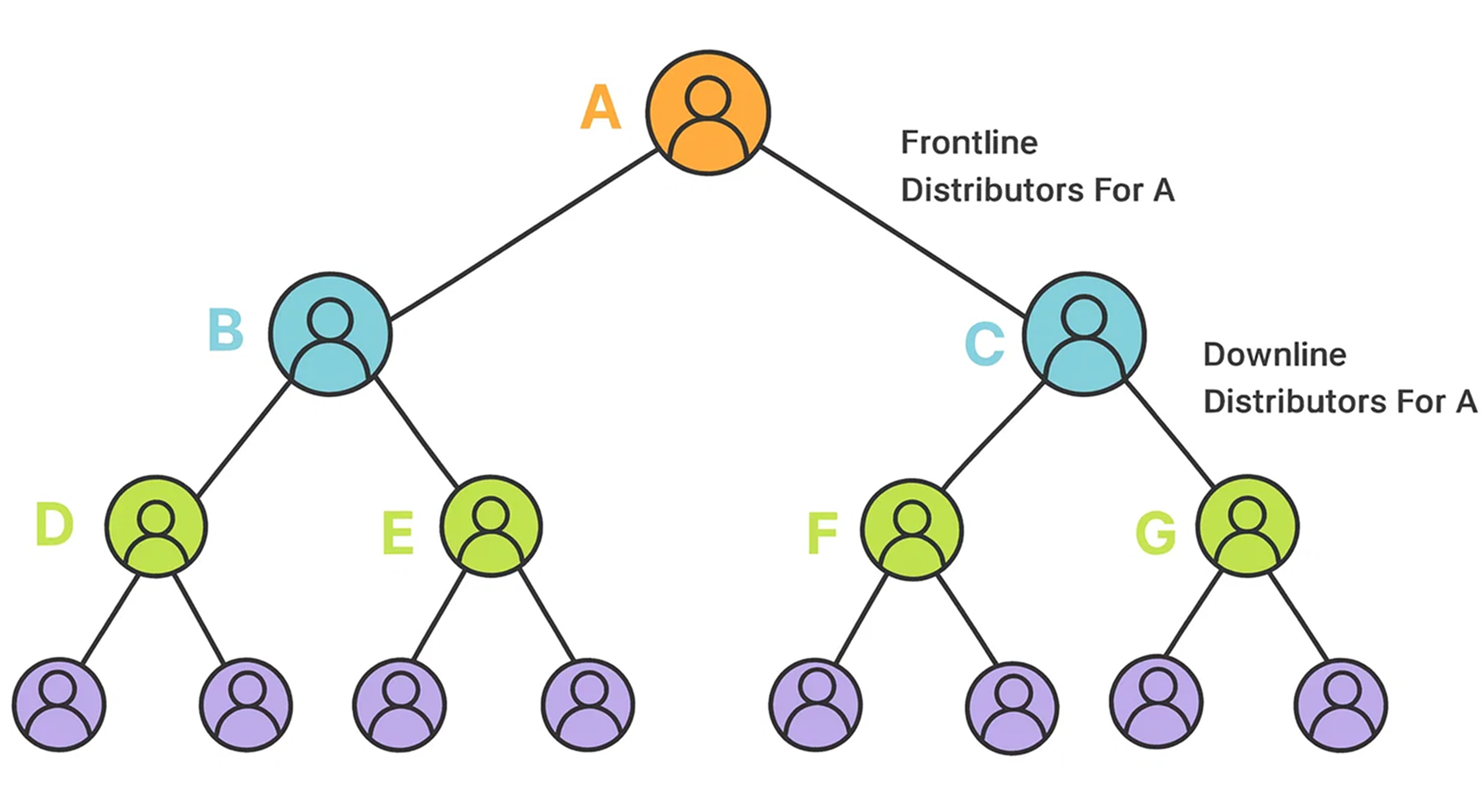
How a Binary MLM Plan Works
Binary MLM compensation plans are simple to grasp, which makes recruiting new members much easier. Instead of paying commissions across multiple levels, earnings are calculated based on the sales volume generated in each of the two legs. In a binary structure, commissions are always based on the “pay leg,” which is the leg with the lower sales volume. The opposite leg, which produces higher volume, is referred to as the “reference leg.”
Distributors in a binary MLM network are encouraged to build and balance both legs because commissions are calculated from the lower-earning leg. When sales are evenly distributed, members can maximize the earning potential of their entire downline. If commissions were based on the higher-earning leg, sponsors would have little reason to support the weaker side, leading to imbalance, reduced growth and eventually stagnation in both sales and recruitment.
The Binary MLM plan enables companies to effectively track their growth and calculate commissions and incentives with greater accuracy. Usually, MLM businesses establish a commission cap for each distributor level in the pay leg by specifying a fixed commission percentage, ensuring predictable and manageable payouts.
Looking to automate your MLM business with a Binary MLM Plan? Use our Binary MLM software to streamline and automate your binary structure. Spillover placements are managed by the MLM company, so preferences may vary. Here are the different types of spillovers in a Binary MLM Plan.
Advantages of the Binary MLM Plan
Endless growth: The Binary Plan allows members to add unlimited levels and boost income potential.
Teamwork: Distributors stay active by balancing the left and right legs to maximize compensation.
Fast growth: Distributors can grow their business quickly with the Binary Plan.
Carry Forward: Any unpaid sales volume from the current binary payout cycle is rolled over to the next cycle.
Disadvantages of the Binary MLM Plan
- Profit margins are directly determined by the activity and engagement of your downline team.
- Maintaining balanced and high-performing legs can sometimes be challenging.
- If the legs become too unbalanced, recruitment may become challenging.
Automate your MLM business with our Binary MLM software and simplify your binary compensation plan.
Different Situations in MLM Binary Plan
Before exploring the different scenarios in a Binary MLM Plan, it’s important to understand a few key terms. The sponsor is the distributor who brings a new member into the binary MLM network, while the parent is the distributor who serves as the direct upline of the new member.
Guidelines for Spillover
Spillover can be implemented in various ways depending on the company’s preference, but generally, there is a structured framework for placing new recruits within the genealogy tree.
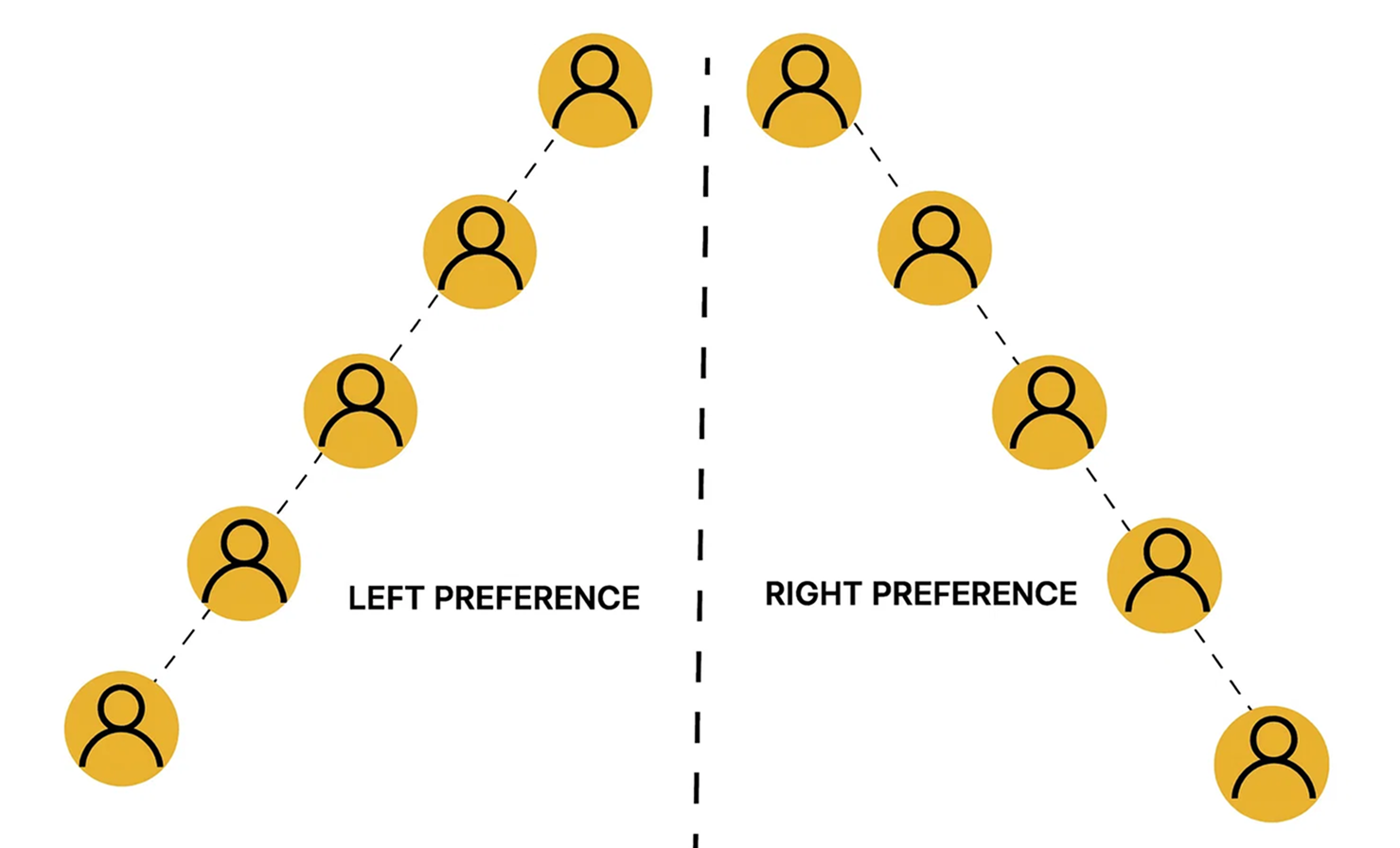
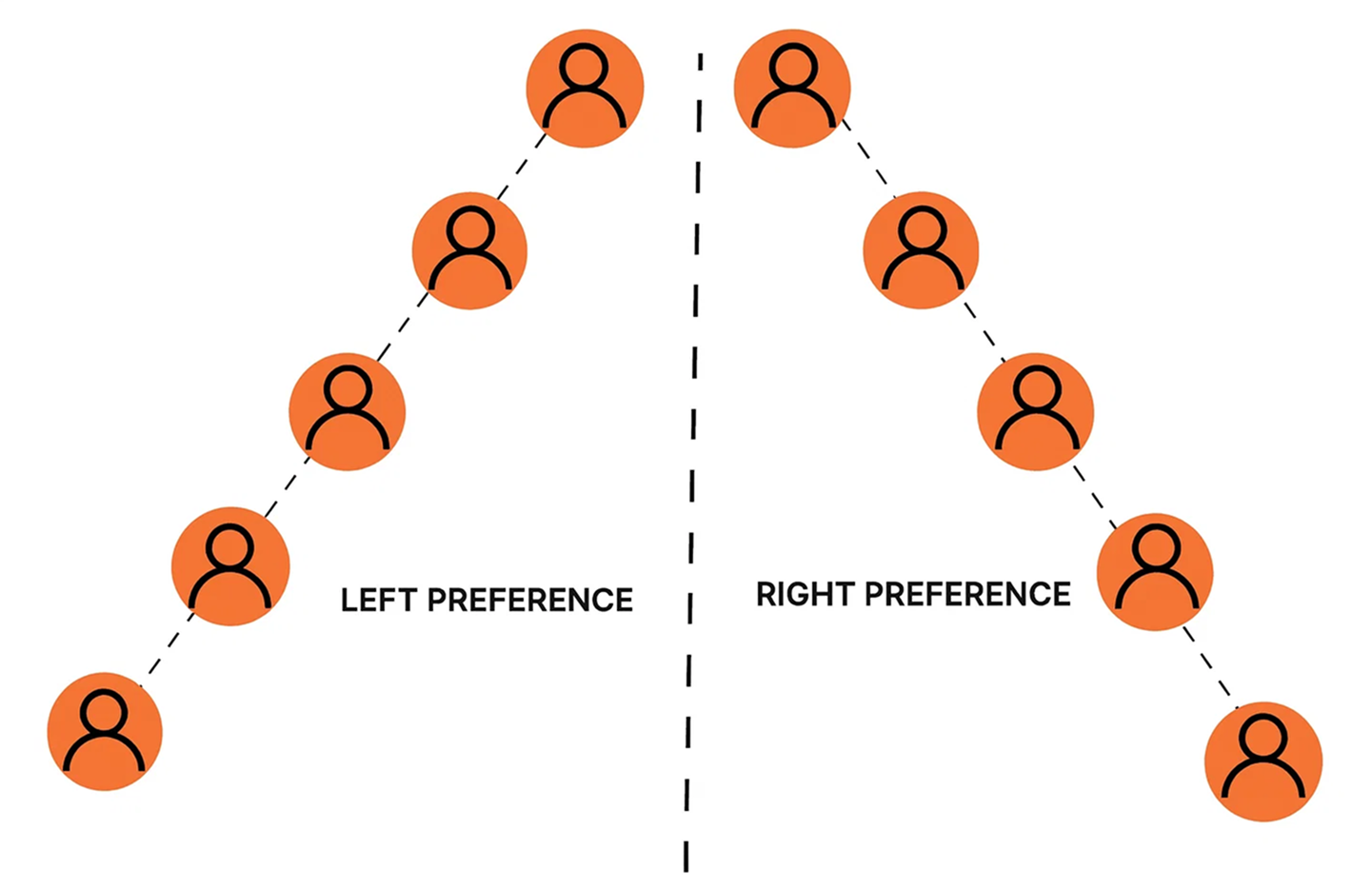
By default, new recruits in a binary MLM plan are typically placed alternately at the extremes of the genealogy tree – first on the far left, then the far right, and continuing this left-right sequence as additional members join. However, based on sponsor preference or company policy, new members can be assigned to any available position within the binary structure.
Below are some common scenarios that occur when sponsors place new recruits at various positions within the genealogy tree of a Binary MLM Plan.
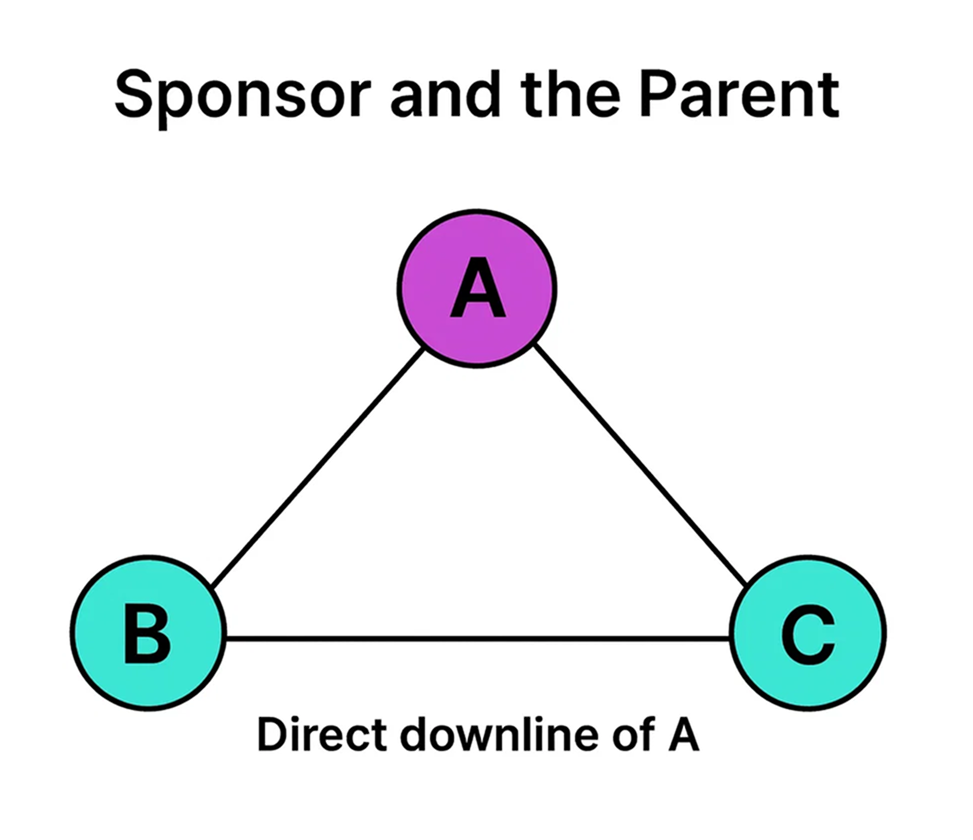
1. The Sponsor And the Parent of downlines are the same
If distributor X sponsors A, and A then adds a new member B to A’s left leg in the binary tree, B becomes A’s direct downline. When A sponsors another member C, the new recruit is placed on A’s right leg, filling the vacant position.
In this setup, B and C are direct down-line of A, with A serving as both their sponsor and parent.
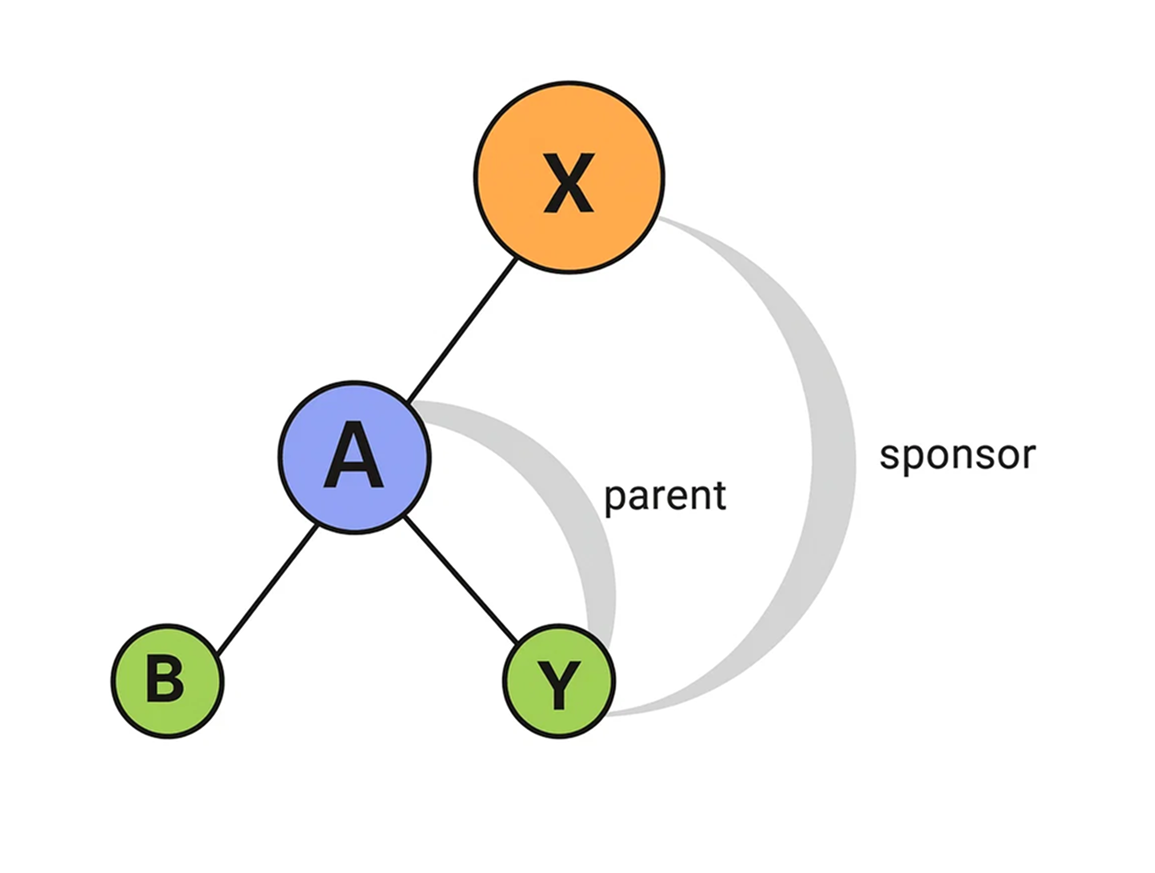
2. The sponsor and the parent of a downline are not the same.
X sponsors A and Y, with Y placed under A’s right leg. When A sponsors a new member B, B is placed under A’s left leg, as that position was vacant.
For Y, A acts as the parent while X is the sponsor. In this case, the sponsor and parent are different. A’s binary structure is built through both their own efforts and the upline’s (X) efforts via the spillover of member Y.
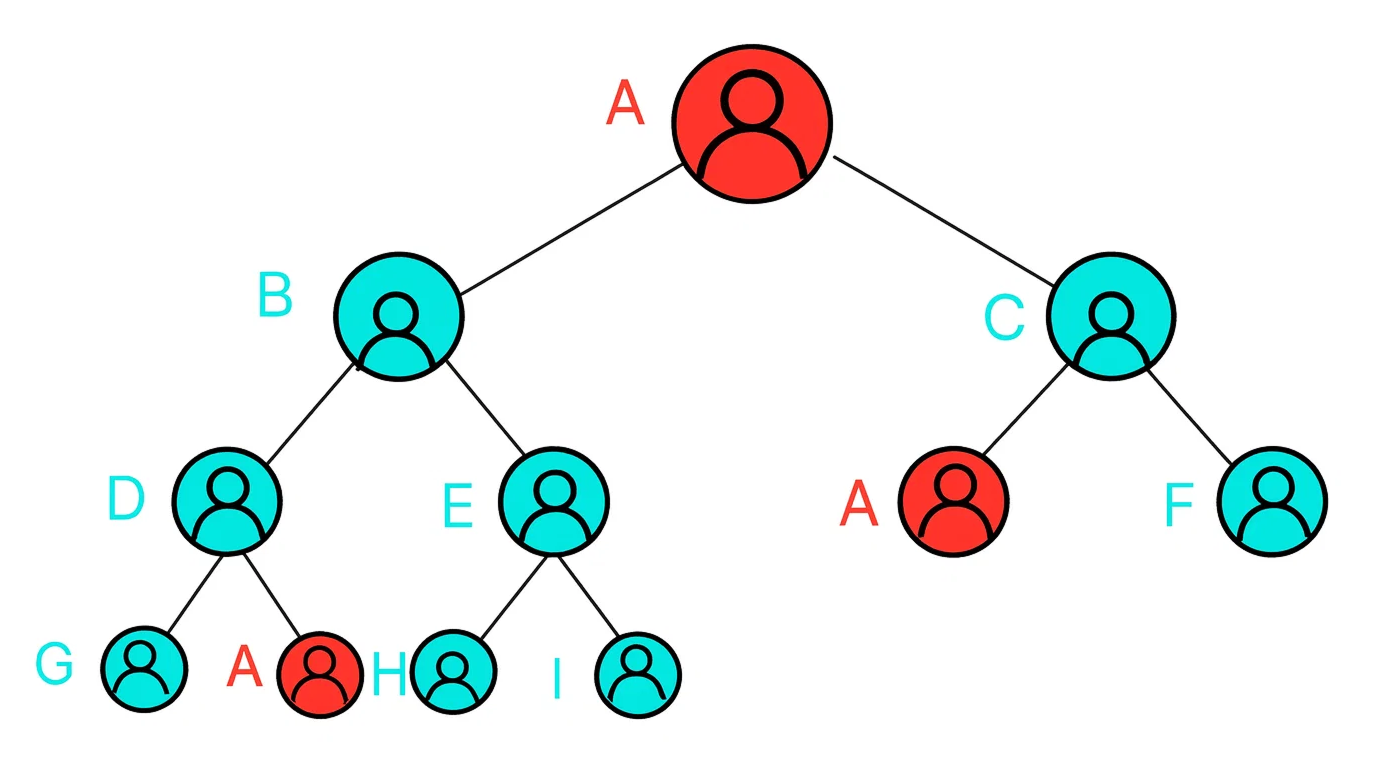
3. Spillover in a Partially Formed Binary
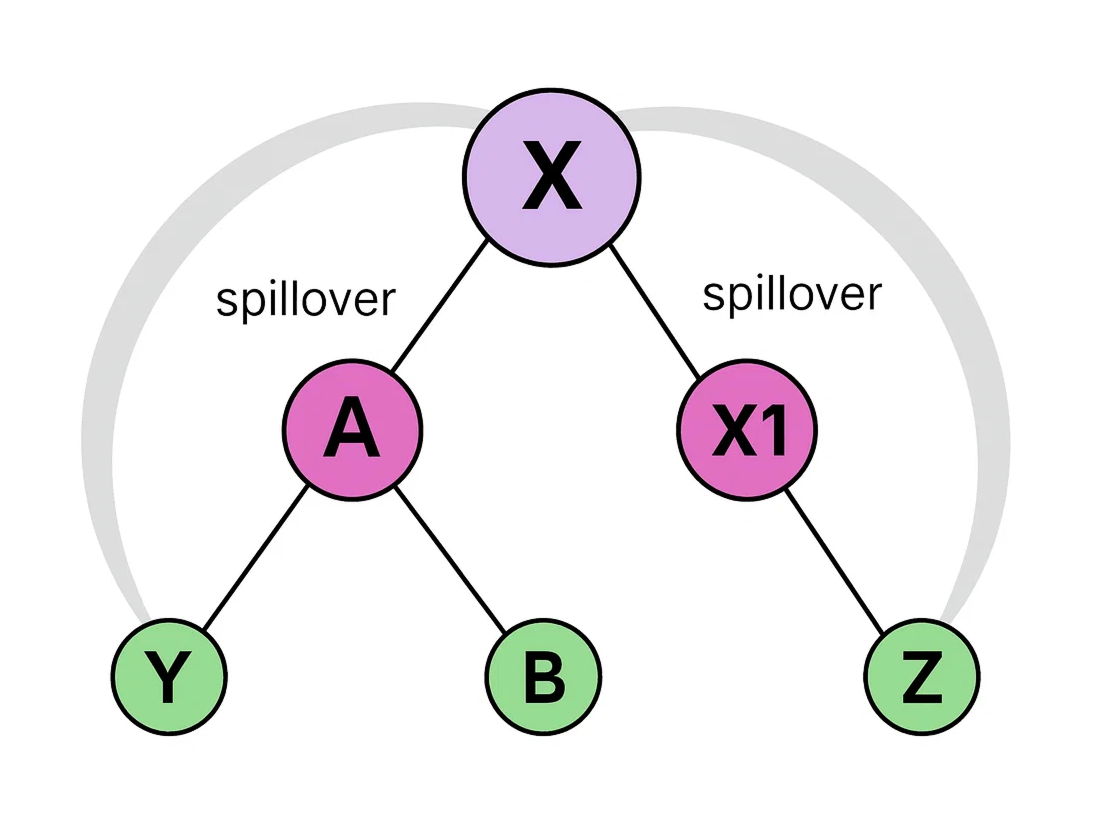
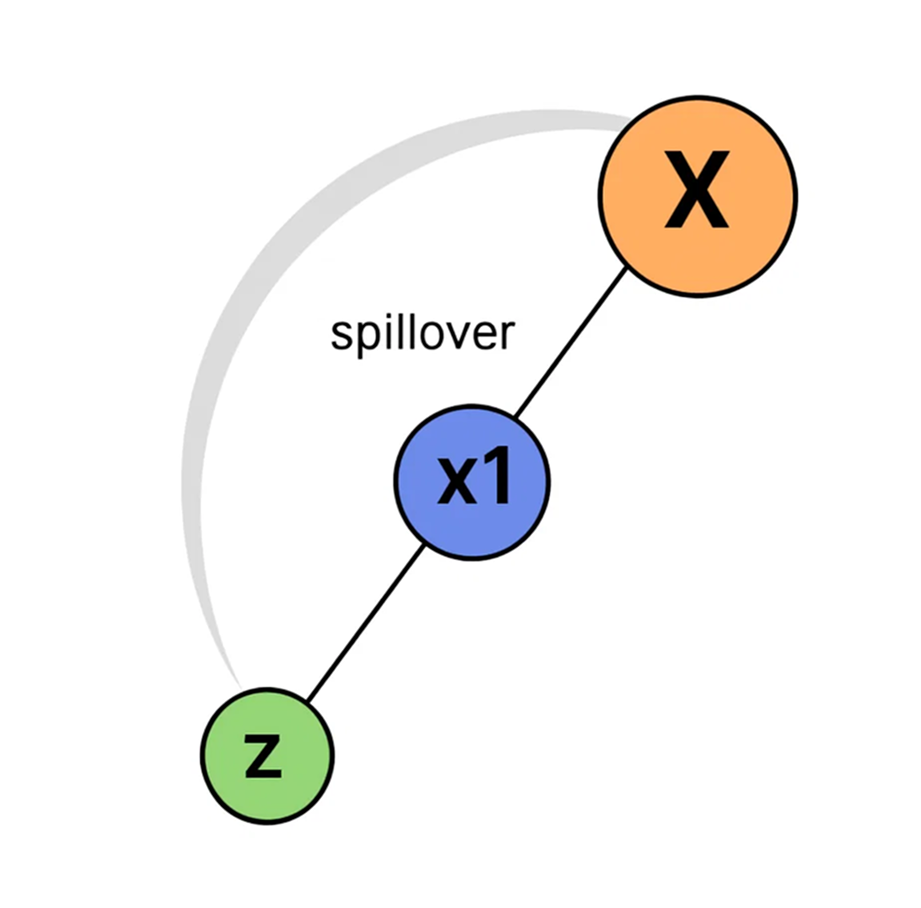
Distributor X sponsors two new members, A and X1, placing them on the right and left legs of X’s binary structure, thereby completing X’s binary formation.
Now, A sponsors a new member B and places them on the right leg, as A’s left position is already occupied by Y, who was previously sponsored by X. X also sponsors Z, placing them to the right of X1. Both Y and Z act as spillovers and are positioned under the downlines of X, A, and X1. Specifically Y is placed under the left down-line of X and A, while Z is placed under the right down-line of X and X1.
In this scenario, two spillovers occur on either side of X, even though the binary structure on both sides is not yet fully formed.
4. Sponsoring exclusively to left leg of the binary structure
In this scenario, A sponsors two new members, B and C. B is positioned on A’s direct left leg, and C is placed on B’s direct left leg. In this case, C acts as a spillover and is positioned at the extreme left.
5. Normal spillover in binary structure
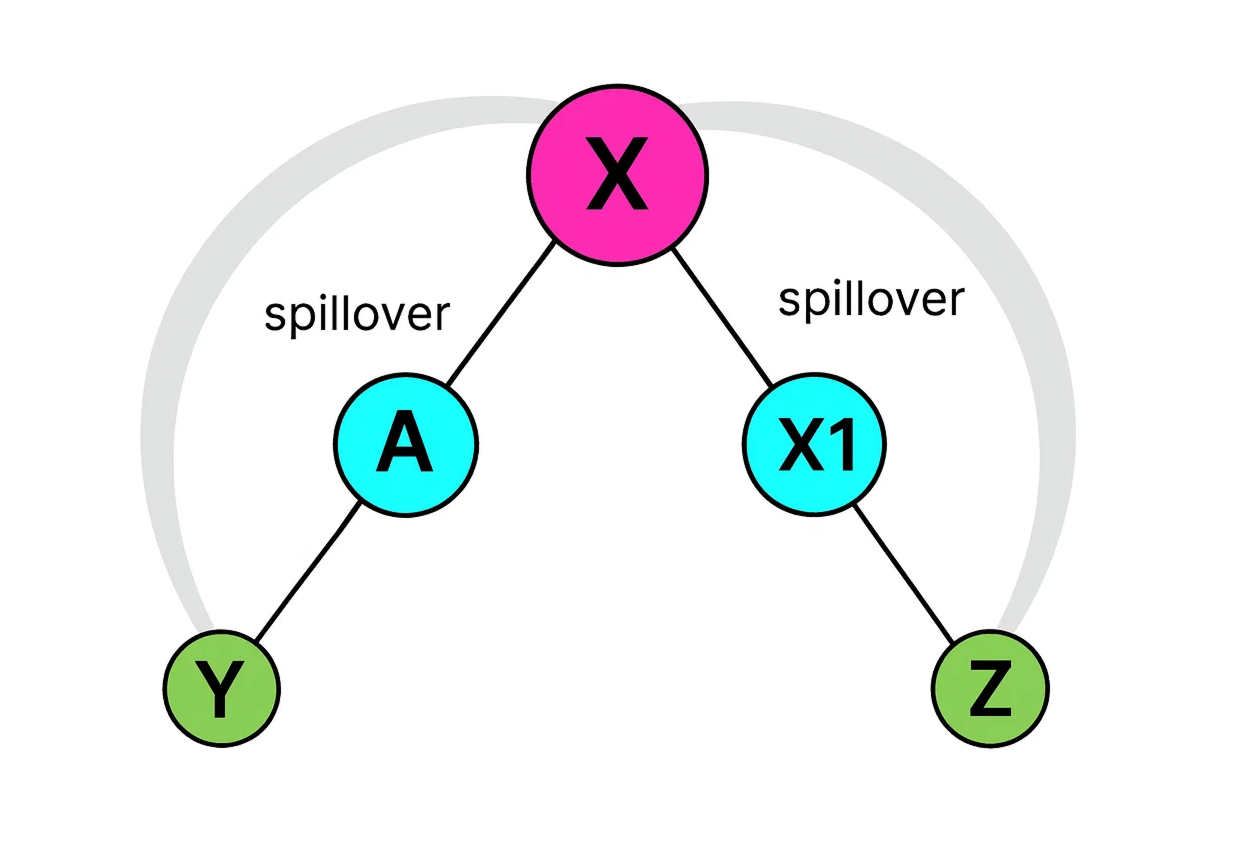
When both the left and right legs of a member are filled, any additional new members sponsored are placed on the next level as spillovers. This is known as normal spillover.
For example, when distributor X sponsors members A and X1, X’s binary structure is complete. If X later sponsors Y and Z, these new members are positioned on the next level as normal spillovers.
Build Your Team Smarter with Our Binary MLM Software!
Different Spillover Types in a Binary MLM Plan
Once a distributor’s binary structure is complete by adding two members to the left and right legs any additional members sponsored by the distributor are placed in the next available positions as spillovers.
Spillover placement is determined by the MLM company, so the rules and preferences may vary from one company to another. The following are the different types of spillovers in a Binary MLM Plan.
1. Extreme End Spillover
Spillover placement can be set to either the extreme left or extreme right leg of the Binary MLM structure. This method is commonly preferred by MLM companies because it encourages distributors to stay active, balance their legs with sales volume, and maximize their binary commissions. Overall, it promotes teamwork and drives higher sales performance.
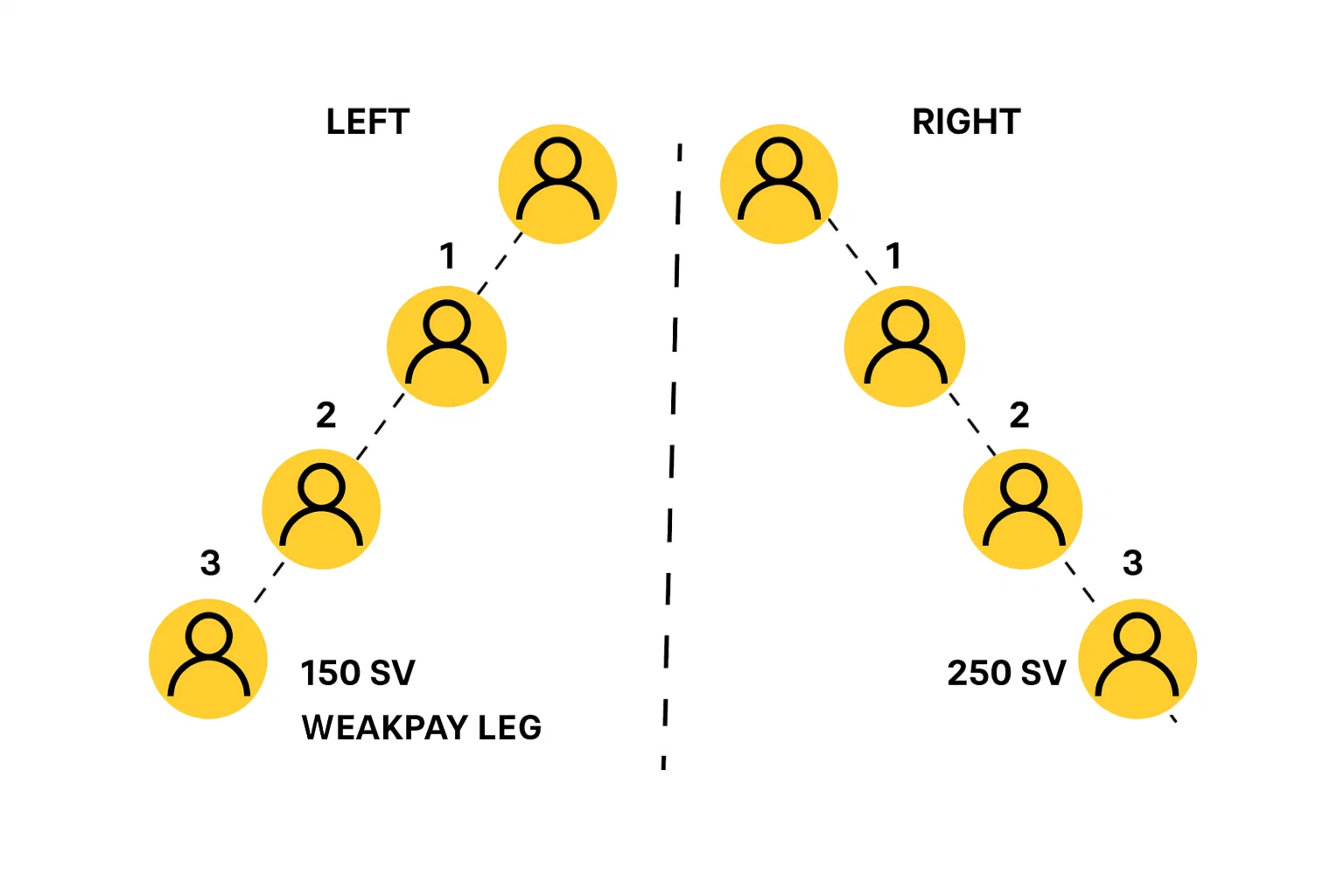
2. Weaker Leg Spillover
Newly added members are placed under the weaker leg of the binary MLM structure. The weaker leg—whether left or right—is determined by whichever side has lower sales volume. This approach is used to help strengthen that leg by boosting its overall sales volume through new recruit activity.
3. Balanced Ratio Spilling
In this spillover method, new members are distributed evenly between both legs to maintain balance, avoid one leg becoming dominant, and ensure fair commission and bonus allocation. This approach helps create a more stable and sustainable MLM business.
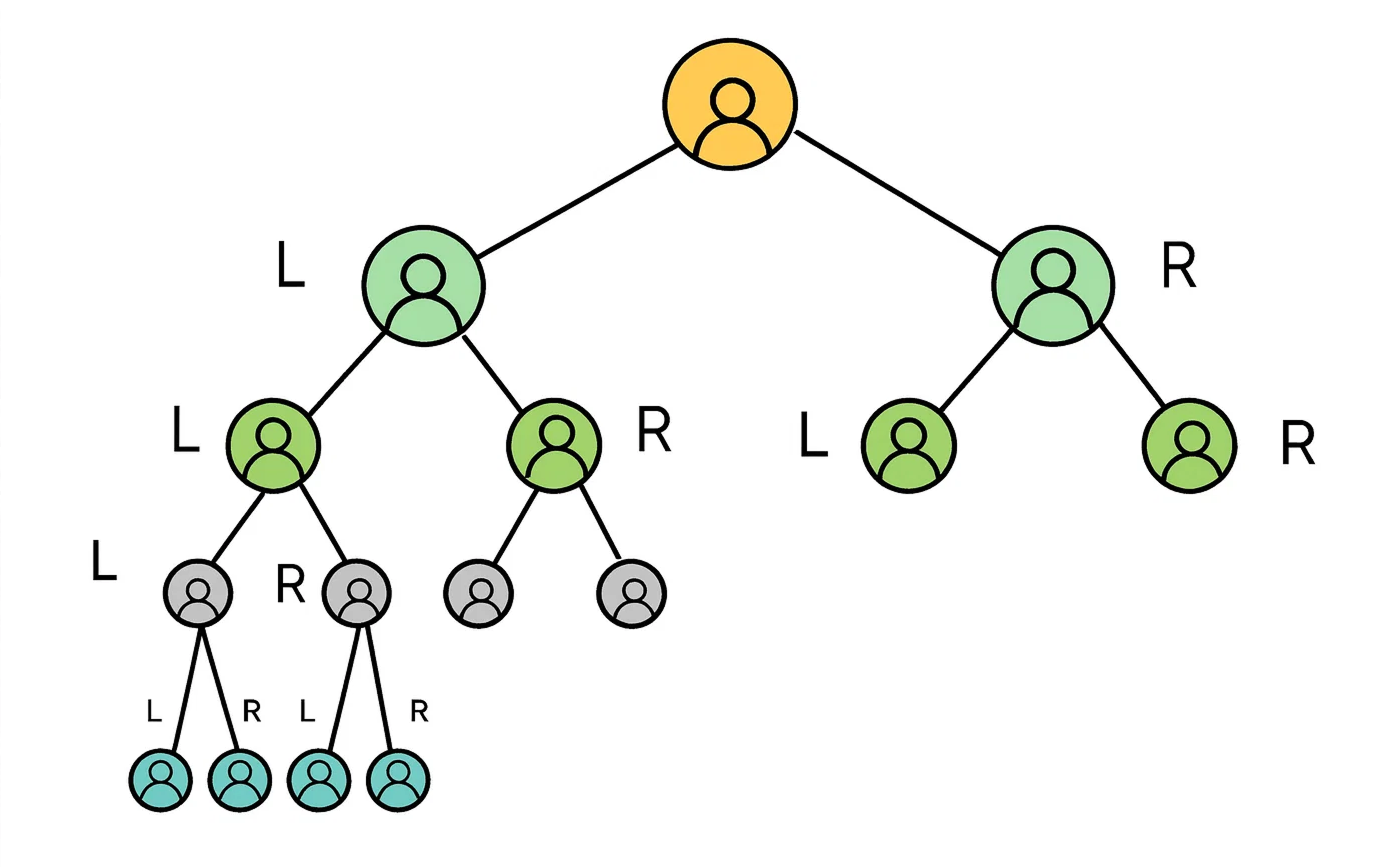
4. Multi-Position Spillover
The distributor may receive multiple positions in the binary MLM structure based on the chosen joining package. Once the first three positions in the binary plan are filled, the subsequent positions are assigned through spillover. This type of spillover placement is typically provided by leading binary MLM companies depending on the distributor’s joining package.
Commission Calculation Methods
Weak-leg Binary Commissions
Binary commissions are paid on the leg that carries the lowest volume, known as the weak leg.
Weak Leg (Sales Leg): The leg with lower sales volume in a binary structure is called the weak leg. Binary commissions are determined based on this leg, which can be either the left or right side depending on Sales Volume (SV).
Strong Leg (Profit Leg): The leg in a binary structure that carries the higher sales volume is referred to as the strong leg.
Sales ratio based binary commissions:
Some companies determine binary commission payouts based on sales ratios or pairing ratios. The most commonly used pairing or sales ratios in a binary plan include:
- 1:1 sales ratio
- 1:2 or 2:1 ratio
- 2:3 or 3:2 ratio
Note: In a binary MLM plan, commissions are issued–or the payout cycle is scheduled–on a daily, weekly, monthly or other periodic basis.
1:1 Sales Ratio: Commissions are paid when the sales volume of the left and right legs reaches a matching 1:1 ratio.
1:2 or 2:1 Plan: Binary commissions are paid when the left and right legs reach either a 1:2 or 2:1 sales volume ratio.
2:3 or 3:2 Plan: Commissions are paid when the left and right legs reach a 2:3 or 3:2 sales volume ratio.
What Is Binary Capping?
Binary capping is a limit set by binary MLM companies to ensure financial stability. If commission payouts exceed control, it can impact the company’s overall turnover. The capping amount is determined based on the binary MLM commission structure or sales volume.
Types of Binary Capping
1. Binary Capping Determined by Sales Volume
This value is determined based on the distributor’s sales volume in relation to their joining package.
For example: If Distributor X earns 200 SV on the left leg and 400 SV on the right leg, and the binary capping is set at 100 SV, then the binary commission will be calculated only on the capped value of 100 SV. The remaining 100 SV from the weak leg and 200 SV from the strong leg are discarded and will not carry over to the next binary commission cycle.
Companies may set this capping on a daily, weekly or monthly basis.
2. Binary Capping Determined by Commission
This value is determined based on the MLM binary plan commission earned by distributors in relation to their joining package.
For example: If Distributor A join with a $1,000 package, the company may set a commission capping of $5,000. The distributor will not earn more than $5,000 in commission. This capping can be applied on a daily, weekly or monthly basis.
Bonuses in a Binary MLM PLan
Matching Bonus : This bonus is awarded to distributors when their personally sponsored members earn a commission. The distributor also receives a percentage of the commissions earned by their sponsored team members.
Bonus on Binary Commissions: This bonus is awarded based on the sales volume generated in both legs of the binary tree. Many MLM binary plan software systems automatically calculate this commission according to the plan’s formula.
Custom Bonus: This bonus can be customized to meet the needs of a specific MLM company or distributor. It is used to reward top-performing team members or to encourage desired behaviors.
Level-Based Bonus: Also called the Depth Bonus, this reward is given to distributors for achieving a specific depth in their binary tree. For example, a distributor may earn the bonus upon building 10 levels of distributors within their team.
Rank Advancement Bonus: MLM companies typically have multiple distributor ranks, and achieving a higher rank can bring extra bonuses and benefits. The Rank Advancement Bonus rewards distributors who attain a new rank within the binary tree structure.
Return on Investment (ROI): This bonus is designed to reward distributors who make a defined financial investment in their business. For example, a distributor may receive a bonus for spending a specified amount on marketing materials or product inventory.
Boost your MLM business with a binary compensation plan and unlock greater success. Click to learn how!